Myocardial biopsies
What is myocardial biopsy?
A myocardial biopsy is a diagnostic technique that includes the extraction of a small tissue sample from the inner lining of the heart muscle. This sample is then examined under a microscope by a specialized laboratory expert known as a pathologist, who searches for cellular changes that indicate any damage or abnormality in the heart.
Why is it performed?
Myocardial biopsy is mainly suggested for patients who just got their heart transplant. This test will help to detect any signs of organ rejection. The test is also used to diagnose ATTR amyloidosis, heart cancer, heart failure, cardiotoxicity from chemotherapy, heart infections, etc.
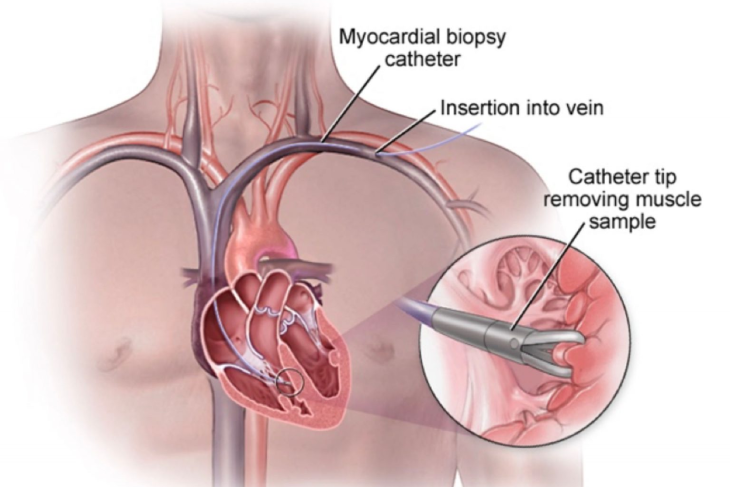
How is it performed?
A catheter will be let into the blood vessel to the heart. The catheter will have a device on its end called a bioptome to snip off and collect the tissue pieces from the heart. The collected tissue samples will be sent to the lab for examinations. The catheter is removed, and the area is bandaged to stop any bleeding.


